Electrical Explosion of Wires (EEW)
In short, EEW or electrical explosion of wire is a synthesis method for metal nano particles that consists of passing a pulse of a high-density current through a wire causing the explosive disintegration of the metal.
In short, EEW or electrical explosion of wire is a synthesis method for metal nano particles that consists of passing a pulse of a high-density current through a wire causing the explosive disintegration of the metal (accompanied by a bright flash of light, a shock wave, the dispersion of the metal, and the fast expansion of a mixture of boiling metal droplets and vapor to the surrounding medium) and the production of metal particles with characteristic sizes down to a few nanometers. During an electrical explosion, a plasma region forms between the electrodes, causing atoms to convert into atomic clusters. These clusters then aggregate to form nanoparticles, typically spherical in shape.
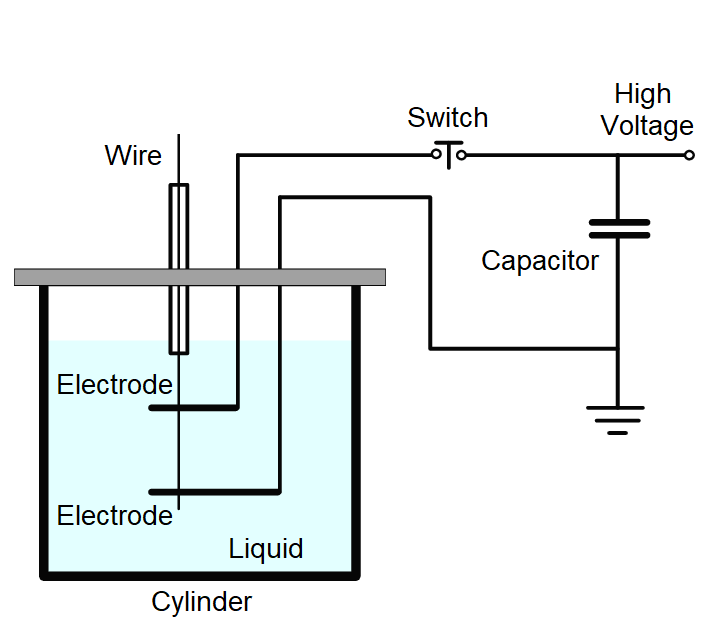
The size and size distribution of the nanoparticles depends on
- type of wire material
- purity of wire material
- the distance between electrodes
- the diameter of the wire
- the amount of the voltage and current applied
- duration of applied energy
- temperature and pressure
“Any conductive material in wire form can be utilized by the EEW method to produce nanoparticles.”
It can utilize metallic wire, metallic alloy wire and even conductive graphite wire/rods and convert them to nanoparticles. The couple of wires can also be used for alloys production.
The media for EEW machine can be:
- Gas: The gas can be inert and also Oxygen, Nitrogen and etc.
- Liquid: The liquid can be water, oil, glycerol, organic liquid, hydrocarbons and etc
In an inert gas environment, nanoparticles remain purely metallic. Conversely, in an oxygen atmosphere, the particles form metal oxides, while in a nitrogen atmosphere, they become metallic nitrides.
PNF Co. has developed two types of equipment based on EEW method to produce metal nano colloids and metal nano powders inside liquid (water or any other liquid media) or gas (Inert or active) chamber. Incorporating EEW technology in both gas and liquid media allows us to tailor our products with exceptional precision, ensuring they meet the specific needs and applications of our clients. The following are our specialty products:
- Nano copper in oil:
Copper Synthesized in oily media, such as glycerol and motor oil, demonstrates remarkable stability due to the presence of carbon particles and coatings on the copper particles. This carbon phase is generated by plasma within the hydrocarbon medium, enhancing the efficiency of the resulting lubricant.
- Al, Fe (nZVI) and Mg active nanopowders (gas media)
Active nanopowders synthesized in a gas media exhibit unique properties that make them highly effective in various applications. These nanopowders demonstrate exceptional reactivity and catalytic abilities due to their high surface area and nanoscale dimensions. Al nanopowders are particularly noted for their energy storage and release capabilities. Fe (nZVI) is widely used in environmental remediation for its ability to degrade contaminants, while Mg nanopowders are valued for their lightweight and high-strength properties in structural applications. Together, these materials represent a significant advancement in nanotechnology, offering innovative solutions across multiple industries.
- Au, Pd and Pt nanopowders
Highly pure nanopowders of gold (Au), palladium (Pd), and platinum (Pt) can be achieved efficiently without the need for chemical reactions or subsequent washing processes. This innovative approach not only ensures the superior quality of the nanopowders but also simplifies the production process, making it more streamlined and environmentally friendly.
- Ta and Tantalum oxide
Amorphous tantalum oxide, a key material in various applications, is readily produced through the electrical explosion of wire (EEW) in a gaseous environment. This method addresses market demand efficiently, delivering high-quality tantalum oxide with desired properties.
- Mo and molybdenum oxide
Molybdenum and molybdenum oxide can be efficiently produced through the electrical explosion of wire within a gas medium. This method ensures high yield and purity, making it a preferred technique for obtaining these materials in various industrial applications.
Candidate material | EEW (liquid media) | EEW (gas media) | ME |
Copper | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
Ni Hydroxide | ✔ | ✔ | |
Ni hydroxide-Ni core-shell | ✔ | ||
MoO3 | ✔ | ||
W oxide | ✔ | ||
W | ✔ | ||
Au | ✔ | ✔ | |
Pt | ✔ | ✔ | |
Ag | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
Al | ✔ |
| |
AlOOH | ✔ | ✔ | |
ZnO | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
Ta oxide | ✔ | ||
Alloys | ✔ | ✔ |
